Electromyography (EMG) Testing
Electromyography (EMG) measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve's stimulation of the muscle. The test is used to help detect neuromuscular abnormalities. The test is very useful for patients that start with orthopedics for injuries, as well as joint or spine pains. EMG tests can detect nerve damage that may also be present and provides the opportunity to shift to a treatment protocol that can prevent loss of function or disability if not otherwise detected.
Dr. Cleeremans personally performs EMG/NCV studies in the office. He is board certified in this procedure and his lab is accredited with “Exemplary Status” by the AANEM (American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine). Other neurological testing and imaging studies are performed at Hoag Medical Facilities and other facilities contracted by the various insurance companies that patients are under.
Why am I being sent to the EMG Lab for tests?
You are being sent to the EMG lab because you have numbness, tingling, pain, weakness, or muscle cramping. Some of the tests that the EMG doctor may use to diagnose your symptoms are nerve conduction studies, needle EMGs, and evoked potentials. The EMG doctor will examine you to decide which tests to do.
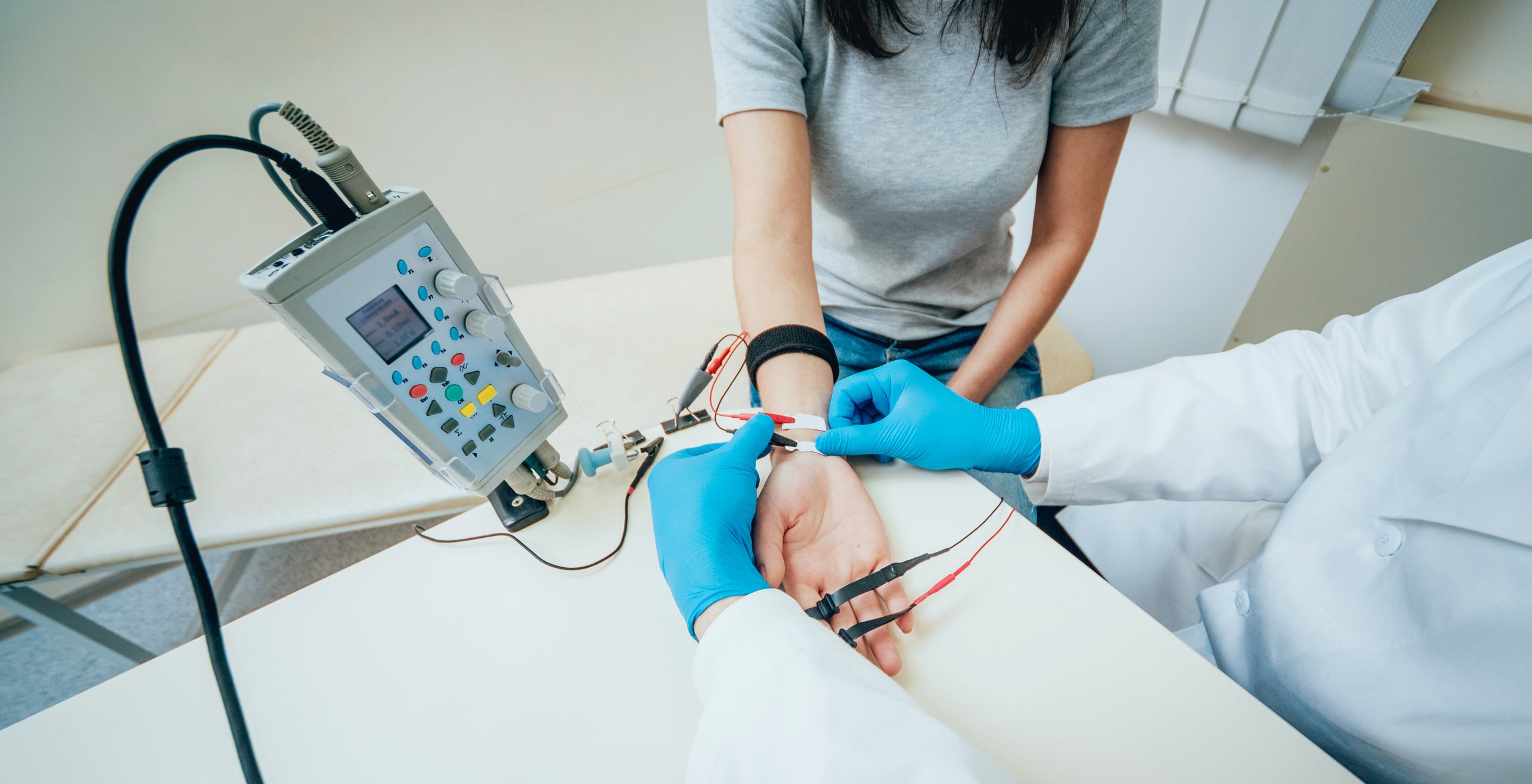
What does an NCS show?
Nerve conduction studies show how well the body’s electrical signals are traveling to a nerve. This is done by applying small electrical shocks to the nerve and recording how the nerve works. These shocks cause a quick, mild, tingling feeling. The doctor may test several nerves.
What happens during a needle EMG?
For this test, a small, thin needle is inserted into several muscles to see if there are any problems. It is used once for each patient and is thrown away after the test. There may be a small amount of pain during this part of the examination. The doctor tests only the muscles necessary to decide what is wrong. During the EMG test the doctor will be able to hear and see how your muscles and nerves are working by the electrical signals made by your muscles. The doctor then uses his medical knowledge to figure out what could be causing your problem.
What is an Evoked Potential?
Evoked potentials are painless tests that check the nerve pathways through the spinal cord or from the eyes and ears. The signals for these tests can come from small electrical shocks, light pulses, or clicks of sound in the ears. The nerve responses are recorded over the scalp and other areas of skin.
How long will these tests take?
The tests usually take 20 to 90 minutes. You can do any of your normal activities, like eating, driving, and exercising, before the tests. There are no lasting side effects. You also can do your normal activities after the tests.
How should I prepare for the tests?
Tell the EMG doctor if you are taking aspirin, blood thinners (like Coumadin®), have a pacemaker, or have hemophilia. Take a bath or shower to remove oil from your skin. Do not use body lotion on the day of the test. If you have myasthenia gravis, ask your EMG doctor if you should take any medications before the test.


